Ever felt like you were trying to read a foreign language when looking at a computer’s specifications? Terms like i5, 16GB RAM, 512GB SSD can sound like meaningless gibberish to the uninitiated. This confusion is a common problem for many buyers, and it often leads to purchasing the wrong device—either by overspending on features you don’t need or by buying a computer that can’t handle your daily tasks. This guide is designed to translate that technical jargon into plain, easy-to-understand English. By the end of this article, you will be able to confidently read any spec sheet and choose the perfect computer for your needs.

A computer is a complex machine, but it can be broken down into a few key components that determine its performance. The “Big 7” essential components are the Processor (CPU), Memory (RAM), Storage, Graphics (GPU), Display, Battery, and Ports. Each of these parts plays a crucial role in how your computer functions, and understanding how they work together is the first step to becoming a savvy buyer.
Interactive Tool #1: Spec Sheet Decoder
Paste a computer’s spec sheet below, and we’ll highlight and explain each component in plain English.
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is often called the “brain” of the computer. It’s responsible for processing instructions and performing calculations, which ultimately determines the overall speed and responsiveness of your device. The two main brands you’ll encounter are Intel and AMD. Both offer a range of processors at different performance tiers, from entry-level to extreme.
Key CPU Terms Explained
| Processor Tier | Intel Equivalent | AMD Equivalent | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level | Core i3 | Ryzen 3 | Basic tasks (web, email, documents) |
| Mid-Range | Core i5 | Ryzen 5 | Most people (multitasking, light gaming, photo editing) |
| High-End | Core i7 | Ryzen 7 | Power users (video editing, 3D modeling) |
| Extreme | Core i9 | Ryzen 9 | Professionals (extreme performance, workstations) |
Interactive Tool #2: CPU Decoder Tool
Enter a CPU model to get a detailed breakdown of its specifications and performance level.
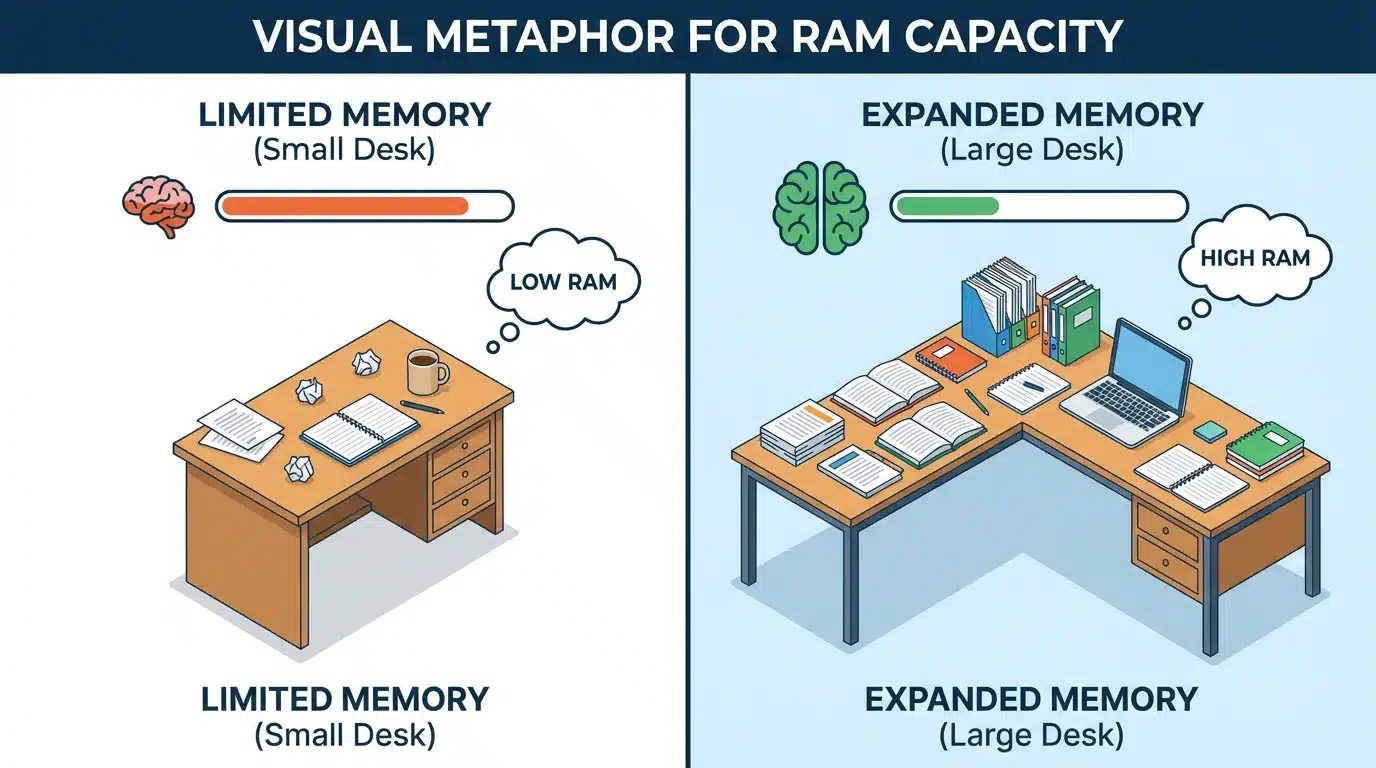
Random Access Memory (RAM) is your computer’s temporary workspace. It holds the data for the applications and files you are actively using. The more RAM you have, the more applications you can run simultaneously without your computer slowing down. Think of RAM as a desk: a larger desk allows you to have more papers and books open at once, while a smaller desk gets cluttered quickly.
How Much RAM Do You Need?
Interactive Tool #3: RAM Calculator
Select your typical activities to get a personalized RAM recommendation.
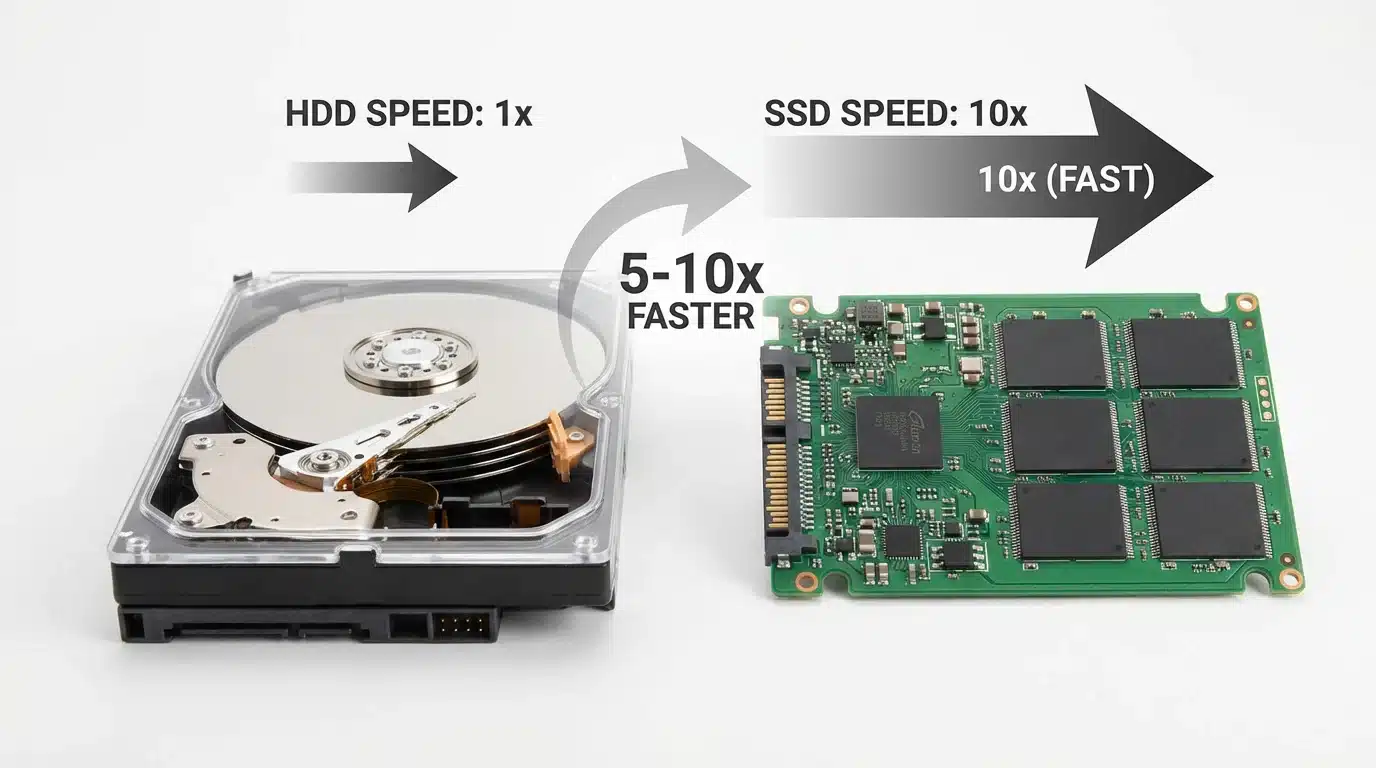
Storage is where all your files, applications, and the operating system are permanently stored. There are two main types of storage: the Hard Disk Drive (HDD) and the Solid State Drive (SSD).
| Feature | HDD (Hard Disk Drive) | SSD (Solid State Drive) |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slow (80-160 MB/s) | Fast (500-3500 MB/s) |
| Boot Time | 30-60 seconds | 10-20 seconds |
| Durability | Fragile (moving parts) | Durable (no moving parts) |
| Noise | Audible spinning | Silent |
| Price | Cheaper ($40/TB) | More expensive ($80-150/TB) |
Interactive Tool #4: Storage Calculator
Estimate how much storage you need based on your file collection.

The Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is responsible for rendering all the visuals on your screen. There are two types of GPUs: integrated and dedicated.
Interactive Tool #5: GPU Needs Assessor
Determine if you need a dedicated GPU based on your primary use case.

The display is one of the most important components, as it’s what you’ll be looking at all the time. Key specs include size, resolution, panel type, refresh rate, and brightness.
Interactive Tool #6: Display Recommender
Get personalized display recommendations based on your needs.
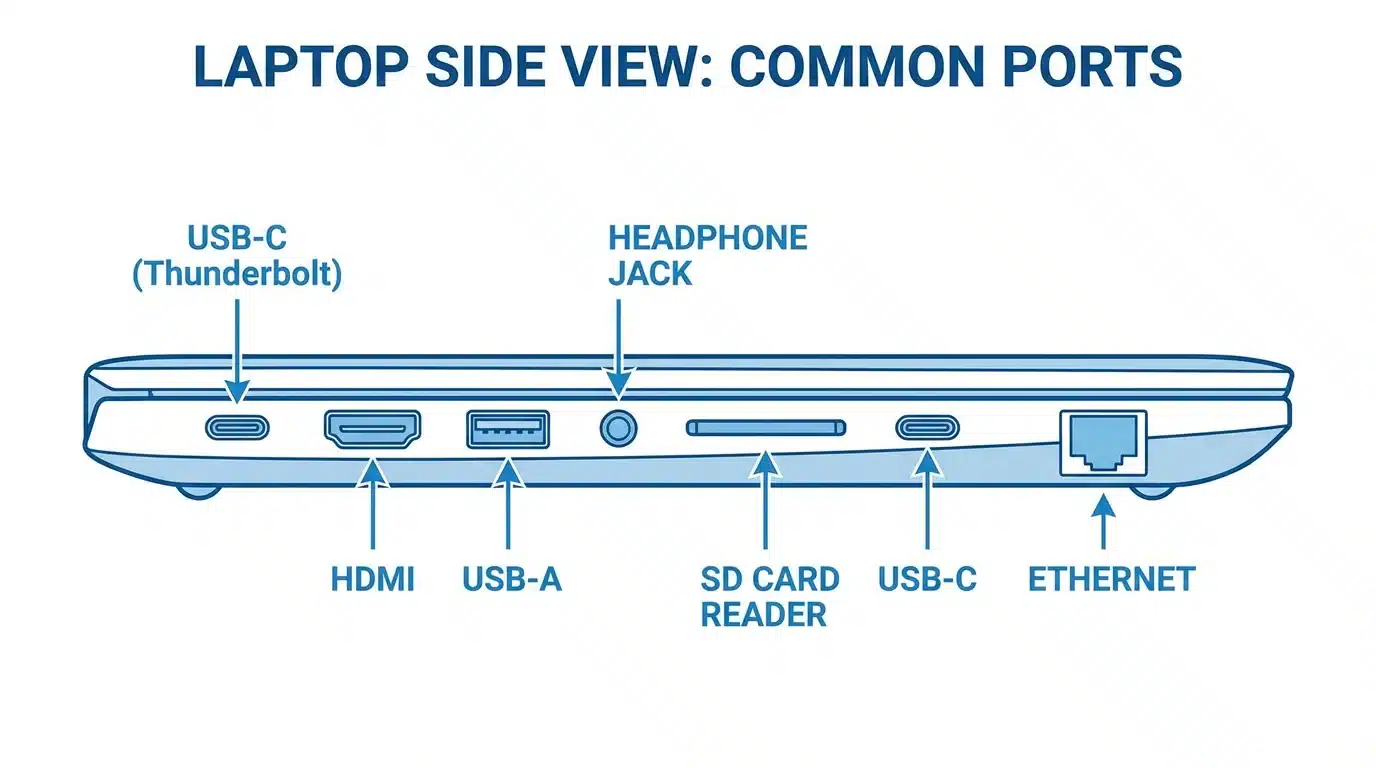
Ports determine what you can connect to your computer. Key ports include USB-A, USB-C, HDMI, and headphone jacks.
Interactive Tool #7: Port Checker
Select your peripherals to see what ports you’ll need.
Interactive Tool #8: Spec Sheet Translator
Paste any spec sheet to get a complete plain-English translation and recommendation.
Interactive Tool #9: FAQ Accordion
Computer specifications are the technical details that describe the hardware components of a computer, such as the CPU, RAM, and storage. They determine the performance and capabilities of the device.
A “good” computer is one that meets your specific needs. A computer with an Intel Core i5 processor, 16GB of RAM, and a 512GB SSD is a great choice for most people.
An Intel Core i5 or AMD Ryzen 5 is a good processor for most laptop users, offering a great balance of performance and battery life.
16GB of RAM is the recommended amount for most users in 2025, as it allows for smooth multitasking and can handle demanding applications.
An SSD is a modern, faster type of storage that makes your computer feel much more responsive than a traditional HDD. SSDs have no moving parts and can read/write data 5-10x faster than HDDs.
You only need a dedicated graphics card if you plan on playing modern games, editing video, or doing 3D modeling. For everyone else, integrated graphics are sufficient.
Full HD (1920×1080) is the standard and provides a sharp, clear image. QHD or 4K resolutions are even better but are only necessary for creative professionals or those who want the absolute best picture quality.
Start by identifying the key components: CPU, RAM, storage, and GPU. Use a guide to understand what each component does and what to look for based on your needs.
For gaming, you’ll want at least an Intel Core i5 or AMD Ryzen 5 processor, 16GB of RAM, a 512GB SSD, and a dedicated graphics card like the NVIDIA RTX 3060 or higher.
For video editing, you’ll want at least an Intel Core i7 or AMD Ryzen 7 processor, 32GB of RAM, a 1TB NVMe SSD, and a dedicated graphics card.
By understanding these key components, you are now equipped to read any computer spec sheet with confidence. Remember to use the interactive tools in this guide to help you make the best decision for your needs. If you’re still unsure, don’t hesitate to contact us for personalized advice. Happy shopping! Check our latest deals for your needs!
Fill out the form below, and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.