Protect Your Business from Cyber Threats with Our Interactive Security Tools
Last Reviewed: October 22, 2025 | By Computer & Laptop Sales

In the digital age, the question is not if your small business will be targeted by cybercriminals, but when. A staggering 43% of all cyberattacks are aimed at small businesses, yet many owners operate under the dangerous assumption that they are too small to be a target. The reality is starkly different. For an Australian small to medium-sized business (SMB), the average cost of a data breach has reached a crippling AUD $276,000.
This guide is designed to be your first line of defense. We will demystify the complex world of cybersecurity, break down the most significant threats, and provide you with actionable, budget-friendly strategies to protect your livelihood. Featuring 10 interactive tools, this comprehensive resource will help you assess your unique risks, calculate your return on security investment, and build a robust defense plan. At Computer & Laptop Sales, we’ve secured over 500 Australian SMBs, and now we’re sharing our expertise to help you fortify your business.
Understanding the enemy is the first step to victory. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, but a few persistent methods account for the vast majority of successful attacks against Australian businesses. Here are the top five threats you need to be aware of.
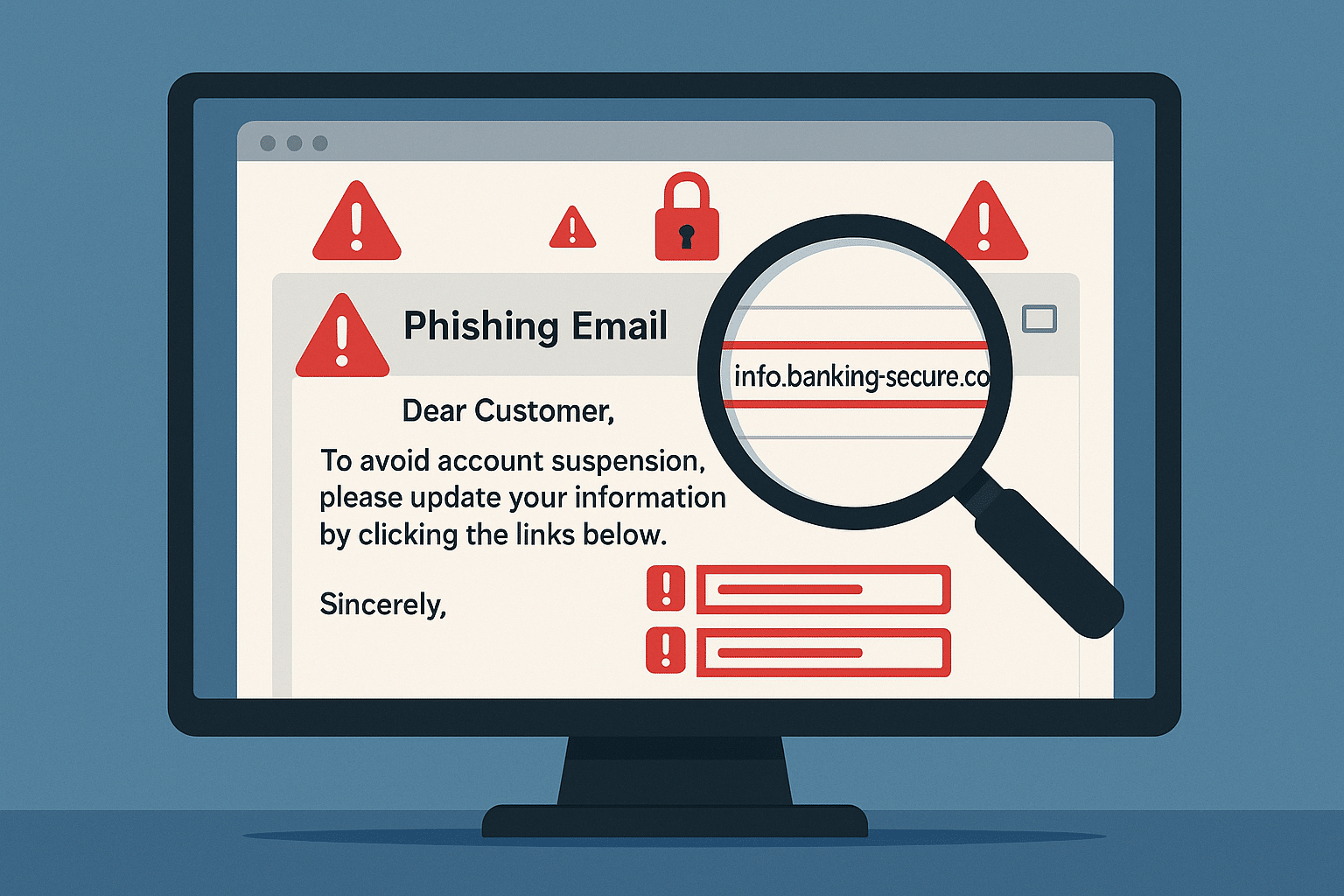
Phishing remains the most common and effective attack vector. These attacks involve deceptive emails, messages, or websites designed to trick employees into revealing sensitive information like passwords or credit card numbers. A classic Australian example involves a fake email from Australia Post, complete with official branding, asking the recipient to click a link to track a package, which then installs malware.

Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts your files, making them inaccessible until a ransom is paid. The average ransom demand can range from $150,000 to over $500,000, and there is no guarantee you will get your data back even if you pay. These attacks can bring a business to a complete standstill for days or even weeks.
In a BEC attack, criminals gain access to a business email account and use it to defraud the company. Common tactics include invoice fraud, where they send fake invoices to your clients, or CEO fraud, where they impersonate a senior executive to authorize fraudulent payments.
Cybercriminals use automated tools to try millions of password combinations (brute-force attacks) or use stolen credentials from other data breaches to gain access to your systems. The widespread reuse of passwords across multiple services makes this a particularly dangerous threat.
Software vulnerabilities are weaknesses in code that can be exploited by attackers. Failing to apply security patches for your operating system (like Windows) and other applications leaves your business wide open to attack.
Take this 10-question quiz to identify which threats pose the highest risk to your business.
Effective cybersecurity doesn’t have to break the bank. Here are five critical security layers you can implement for a relatively low monthly cost.
This is your foundational layer of defense, including antivirus, anti-malware, and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions. These tools protect your computers and devices from malicious software. Recommended Tools: Microsoft Defender for Business, Bitdefender GravityZone, Sophos Intercept X.
Since phishing is the top threat, a dedicated email security solution is essential. These tools provide advanced spam filtering and phishing protection, stopping threats before they reach your employees’ inboxes. Recommended Tools: Mimecast, Proofpoint Essentials, Microsoft 365 ATP.

MFA is one of the most effective security measures you can implement, blocking 99.9% of automated password attacks. It requires users to provide a second form of verification (like a code from their phone) in addition to their password. Recommended Tools: Microsoft Authenticator, Google Authenticator, Duo Security.
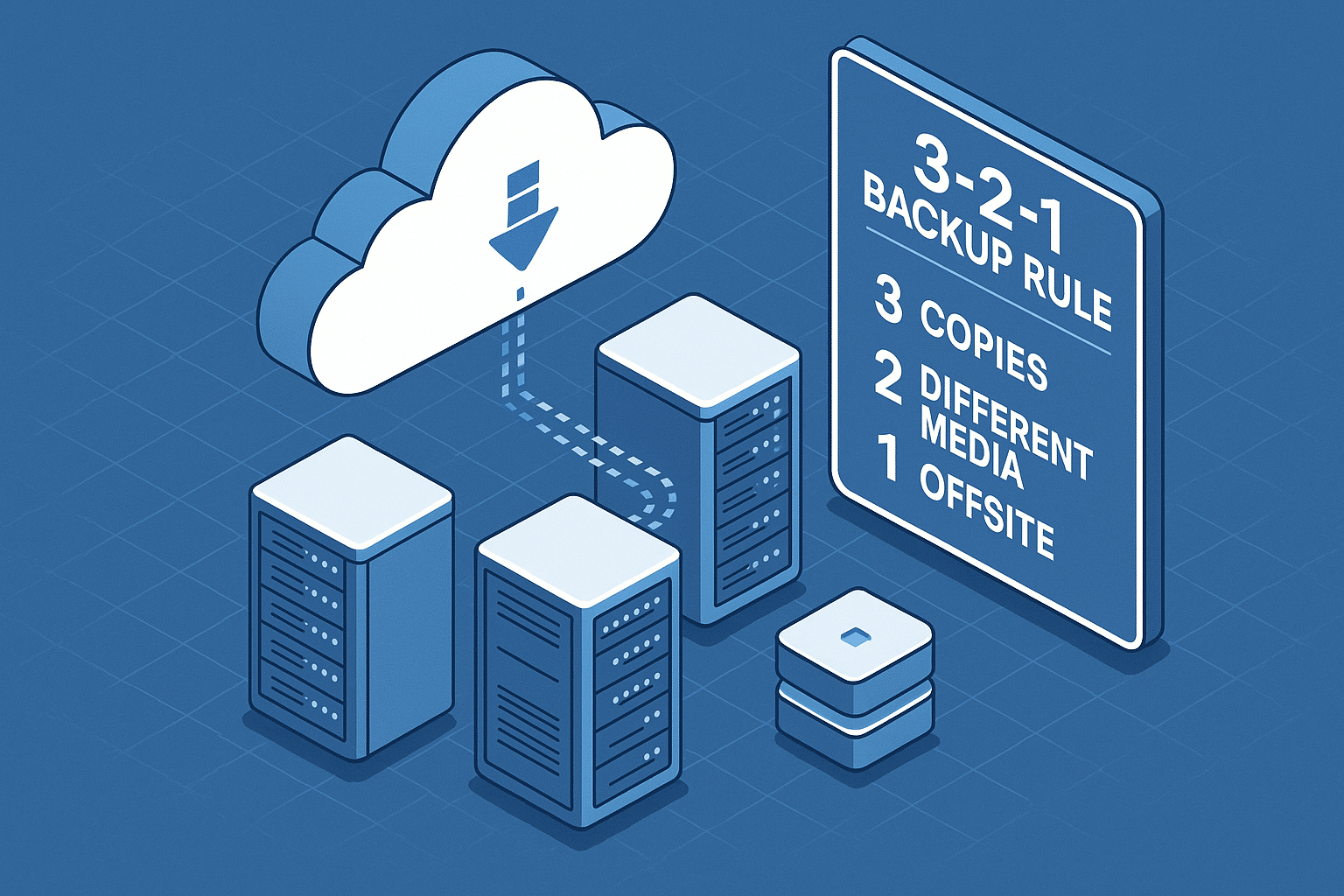
In the event of a ransomware attack or hardware failure, a reliable backup is your only guaranteed way to recover your data. Follow the 3-2-1 backup rule: three copies of your data, on two different media, with one copy off-site. Recommended Tools: Acronis Cyber Protect, Veeam Backup & Replication, Backblaze.
A firewall acts as a barrier between your internal network and the internet, blocking unauthorized access. Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) offer more advanced features like intrusion prevention and application control. Recommended Tools: Fortinet FortiGate, SonicWall TZ Series, pfSense.
Calculate your estimated monthly security costs and ROI.
Estimated Monthly Cost: $0
Annual Cost: $0
Cost of Average Breach: $276,000
ROI: Calculating…
For many small businesses, managing cybersecurity in-house is not feasible. This is where a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP) can be a game-changer.
Managed IT security involves outsourcing your cybersecurity monitoring and management to a third-party provider. They offer 24/7 threat detection, monitoring, and incident response, acting as your dedicated security team.
Compare the 3-year total cost of ownership for in-house vs. managed security.
| Option | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | 3-Year Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-House IT | ||||
| Managed Services |

Technology can only do so much. With 90% of data breaches involving human error, your employees are both your weakest link and your greatest security asset.
Test your password strength in real-time. (Note: Your password is never sent to any server – all checking is done locally in your browser.)

An IRP is a formal document that outlines how your organization will respond to a security incident. Having a plan can reduce the financial impact of a breach by over 50% and is often a requirement for obtaining cyber insurance.
Here is a prioritized checklist of actions you can take to immediately improve your security posture.
Track your progress as you complete these essential security actions. Your progress is automatically saved.
0% Complete (0/25 items)
Immediate Actions (Do Today)
This Week
This Month
Ongoing
Navigating the legal landscape is a critical part of cybersecurity in Australia.
Cybersecurity is not a one-time fix; it is an ongoing process of assessment, protection, and adaptation. By understanding the threats, implementing layered security measures, and training your employees, you can significantly reduce your risk and protect the business you have worked so hard to build. Use the interactive tools in this guide to start your journey to a more secure future.
Ready to take the next step? Get a free security audit, or contact our team for a no-obligation consultation on our managed security services.
The top five cyber threats facing Australian small businesses are: 1) Phishing and social engineering (35% of breaches), 2) Ransomware (23% of breaches), 3) Business Email Compromise/BEC (18% of breaches), 4) Weak passwords and credential theft (15% of breaches), and 5) Unpatched software and vulnerabilities (9% of breaches). Phishing remains the most common attack vector, using deceptive emails to trick employees into revealing sensitive information.
A small business should budget between $20-$50 per employee per month for basic cybersecurity measures, which includes endpoint protection ($5-15/user), email security ($3-10/user), multi-factor authentication (free-$5/user), backup and recovery ($10-30 total), and firewall/network security ($50-200 total). For comprehensive managed security services, expect to pay $200-500 per user per month.
While not legally required, cyber insurance is highly recommended for Australian small businesses. It can cover costs associated with data breaches, including legal fees, notification costs, forensic investigations, and business interruption. Most insurers require you to have certain security measures in place, such as MFA and a formal incident response plan.
The Essential Eight is a set of baseline cybersecurity mitigation strategies recommended by the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC). The eight strategies are:
1. Application Control
Prevent execution of unapproved/malicious programs including .exe, DLL, scripts (e.g., Windows Script Host, PowerShell and HTA) and installers.
2. Patch Applications
Update applications such as Flash, web browsers, Microsoft Office, Java and PDF viewers. Patch/mitigate computers with “extreme risk” vulnerabilities within 48 hours.
3. Configure Microsoft Office Macro Settings
Block macros from the internet, and only allow vetted macros either in ‘trusted locations’ with limited write access or digitally signed with a trusted certificate.
4. User Application Hardening
Configure web browsers to block Flash (ideally uninstall it), ads and Java on the internet. Disable unneeded features in Microsoft Office (e.g., OLE), web browsers and PDF viewers.
5. Restrict Administrative Privileges
Provide privileges only to users who need it and only for the time they need it. Regularly revalidate the need for privileges. Don’t use privileged accounts for reading email and web browsing.
6. Patch Operating Systems
Update operating systems of workstations, servers and network devices. Patch/mitigate computers with “extreme risk” vulnerabilities within 48 hours. Use the latest operating system version.
7. Multi-Factor Authentication
Require an additional factor (something users have) to prove their identity in addition to a password (something they know). The additional factor should not be able to be stolen remotely.
8. Regular Backups
Backup important new/changed data, software and configuration settings daily, preferably automatically. Retain backups for at least three months. Store backups offline (i.e., disconnected from computers and networks).
Effective cybersecurity training should be conducted at least quarterly, with monthly refreshers being ideal. Essential topics include phishing recognition, password hygiene, social engineering tactics, and incident reporting procedures. Use simulated phishing tests to measure training effectiveness and consider gamification to increase engagement.